The pandemic, digitalization, and other ongoing events have increased the number of cybercrimes. Hackers want to gain data for political purposes, money stealing, access to technologies, and others. It applies to any sphere, be it eCommerce or manufacturing.
Let’s take an online store as an example. It possesses information about clients, employees, suppliers, and others. So cybercriminals invent numerous ways to gain profit from breaking an eCommerce system. For example, they may create a distributed denial of service (DDoS) attack, harming the servers and increasing Magento server response time or the same metric for your eCommerce platform. Attackers may then ask for a ransom to restore the website’s work.
A cyberattack damages the company from financial to reputational sides. So you should understand the meaning of a cybersecurity risk to take preventive measures and train others to do the same.
What is a cybersecurity risk?
Cybersecurity risks denote the probability of exposing a company’s information and losing control over its systems due to external invasion. As a result, the company loses its money, reputation, or intellectual property.
What does a cybersecurity risk stem from? It can come from:
- unauthorized intentional penetration,
- unintentional data disclosure, or
- accidental system break.
Data breaches, typical cyberattacks, can result from inadequate data protection and significantly harm a business. Online entrepreneurs have to strengthen their security maturity to protect their businesses and customers and minimize the cost of cyberattacks, if any.
The bottom line is that you can’t avoid a cybersecurity threat completely. There is always a high chance of letting the secrets out as criminals’ strategies get more sophisticated every day and the use of technology increases.
A company can get a competitive advantage only if it employs recent solutions, has a robust online presence, and exchanges information across numerous departments: sales, marketing, developers, managers, etc. So the reliance on computers, networks, software, social media, and data increases. All these factors make a business increasingly susceptible to cyber threats.
What are the most common cybersecurity risks?
Gartner points out these seven trends in cybersecurity in 2022:

- Attack surface expansion. It happens due to the work-from-home trend, greater use of the public cloud, and reliance on connected supply chains, leading to more points where attackers can access and steal data.
- Identity system defense. It means companies need to protect their systems from the misuse of credentials which is now a primary method to penetrate corporate networks.
- Digital supply chain risk. It’s an attempt to compromise a vendor’s technology, products, or services, putting its customer base at risk.
- Vendor consolidation. Vendors combine security operations into a single platform to make packaged solutions more appealing and add price and licensing alternatives.
- Cybersecurity mesh. It’s cutting-edge architecture to deploy and integrate security to assets on-premises, in data centers, or in the cloud.
- Distributed decisions. This trend involves separating cybersecurity leaders and sending them to different parts of the organization to decentralize security decisions.
- Beyond awareness. As traditional security awareness training shows unsatisfactory results, progressive organizations develop holistic behavior and culture change programs to improve training outcomes.
Who is responsible for the company’s cybersecurity?
Working on cybersecurity starts with the executive-level managers (or C-suite) within a company. Why? Because a strong security culture entails a never-ending process from the top of the organization. Leaders should explain the importance of cybersecurity risk management, set policies, and plan.
Based on the Statista report, the Chief Information Officer (CIO) was the highest-level employee in the organization who was accountable for cybersecurity in 2021, according to 57% of the respondents.
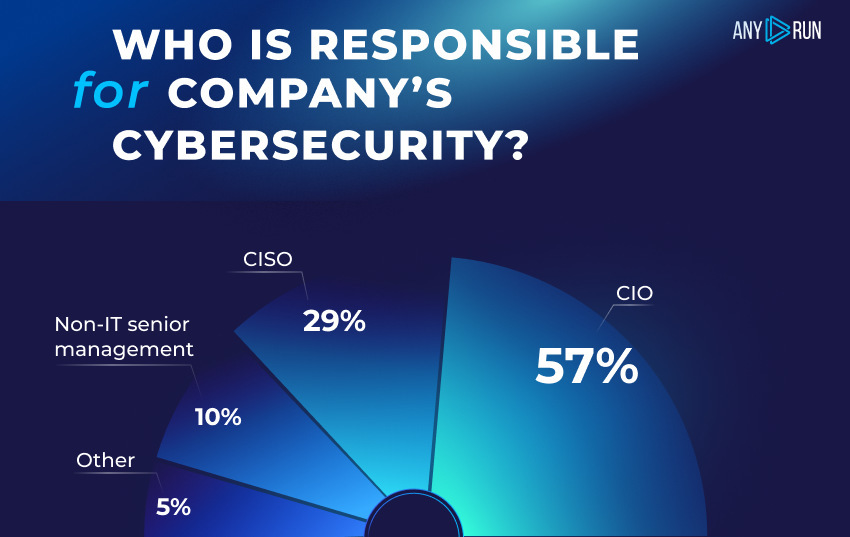
A company with a solid determination to protect its data should also employ a Chief Information Security Officer (CISO). These people are in charge of creating and maintaining the enterprise vision, strategy, and cybersecurity program. They guarantee the adequate protection of information assets and customer data.
Many businesses think that only the IT and security teams should be in charge of managing a cybersecurity risk. Yet, it’s not true.
Any organization needs an effective cybersecurity strategy, such as:
- company-wide awareness program
- a well-established incident response plan
- describing individual roles and obligations and the precise actions that each user or department should take in the case of an attack
- choosing reliable third-party vendors
- analyzing unknown threats in ANY.RUN malware sandbox
- using threat intelligence tools and security programs
This cybersecurity strategy will serve as a guide for how the entire organization should respond to threats. It helps employees see how everyday actions protect or jeopardize corporate data.
How to avoid cybersecurity risks?
1. Encrypt and Back up Data
Make it harder for hackers to read your data. For this purpose, you need to encrypt it rather than store it in a plain-text format. Give the encryption key to a restricted number of users to reduce the chances of a data breach. And even if an unauthorized person succeeds in intercepting your information, they won’t be able to read it.
Plus, back up your data and store it in different locations. When hackers block your systems, it disrupts all operations, leading to significant revenue losses. Data backup may not save you from reputational damage, but it guarantees uninterrupted work if something happens.
THE 3-2-1 RULE MAY HELP:
You need not less than 3 copies of your data and save them in 3 various places.
Keep copies on at least 2 media.
Store at least 1 copy of the data outside the office.
2. Update Systems and Software
Cybersecurity depends on the state of your software. You need to update it to install new features, fix bugs, and introduce new security patches. Dated programs contain weaknesses that are easy to take advantage of.
3. Implement Security Awareness Training
Most cybercrimes happen due to negligence or social engineering. People play a vital role in giving information to others. According to statistics, human error accounts for 95% of cybersecurity problems. What can you do when implementing employee training?
- Analyze your team’s habits and difficulties. You should understand possible threats and align a cybersecurity training with the business plan.
- Determine what needs improvement and how to make that change.
- Design security culture initiatives for each stakeholder group. Once everyone understands the danger, they’ll be able to follow and support you.
- Stress the need to double-check email addresses before sending replies and clicking links.
- Specify what and how employees may share, including on social media.
4. Choose Various Secure Passwords
Other alarming statistics entail the use of passwords. For example, 69% of small companies neglect password policies, increasing the cybersecurity risk in the organization. Employees choose the same simple password for all their accounts and may even share them with others. All these actions simplify the path to the system for cybercriminals.
- Encourage your team to create strong passwords at least eight characters long.
- Employ multi-factor authentication.
- Passwords should contain words with mistakes, letters, numbers, and not personal information.
- People shouldn’t disclose their passwords to others and use them more than once.
5. Mind Physical Security
Physical security is as important as digital. As there are many rules to consider when developing a cybersecurity plan, you may neglect simple recommendations concerning papers, keys, and warning systems. Digital security may be useless if it’s easy for criminals to steal your gadgets or even break into the office. Or consider a case when a janitor may run through the files and gain information about employees or organizations.
You wouldn’t leave your car keys in the ignition for thieves, so don’t do the same with your ID badges, credit cards, personnel, and financial papers, cell phones, and tablets. Instruct employees to hide and lock these things when unneeded.
Utilize reliable protection systems in restricted areas. 2-factor authentication methods like keycards and biometrics also help reduce cybersecurity risks. These measures will prevent anyone from entering the space or seeing critical data.
What problems with establishing a cybersecurity culture may you face?
The first key stumbling block is the lack of proper security funding. Another one is when the company’s top executives don’t support such initiatives. Other issues that security teams confront include:
- Security has a poor reputation. Security teams are not always recognized or understood, so the strategy should improve people’s attitudes regarding protection.
- Conflicts within security teams. Toxicity inside the security teams themselves impacts the whole corporation and can prevent establishing a security culture.
- Finding a CISO who can lead and establish a cybersecurity culture. A good chief security officer must be capable of handling the situation and prioritizing cybersecurity.
Final Word
Browsing the Internet is so deceptively easy that people often fall prey to cyberattacks. They use similar passwords for numerous websites, click on illegitimate links, and believe the fake bank and store representatives. There are two primary reasons why companies can’t cope with cybersecurity risks:
- the rapid shift to digital resources leaving no time to protect data;
- negligence of basic rules, which stems from the lack of education and caution.
The first requires you not to make hectic decisions and install protected software on your corporate devices. The second reason points to the importance of internal education. Both create loopholes for hackers to penetrate systems. As a result, the company faces lawsuits, fines, and discredit. Train your employees on major cybersecurity principles, such as:
- not opening unreliable emails and files;
- updating software;
- creating complex and different passwords without disclosing them to anyone;
- paying attention to cybersecurity when working remotely;
- to name a few.
Employ advanced AI-based technologies for authentication and service for analysis like ANY.RUN malware sandbox and tools for spam identification. Back up the information and download trusted antivirus software. These and more strategies will ensure business prosperity in this digital era.
Alex Husar
Alex Husar is a chief technology officer at Onilab, a full-service eCommerce agency with a focus on Magento. With almost a decade of professional experience, Alex has unique expertise in Magento migration, full-stack development, and PWAs creation. He applies both technical knowledge and management techniques to lead Magento and Salesforce projects.
1 comments








Thank you! It’s so interesting