Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


Revenge was one of the most popular remote access trojans to be used in 2019 when it was featured in a huge malicious campaign named “Aggah”. This malware can take remote control of infected machines and spy after the victims.
|
Trojan
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 January, 2016
First seen
:
|
8 December, 2025
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 January, 2016
First seen
:
|
8 December, 2025
Last seen
:
|

 430
430
 0
0

 2270
2270
 0
0

 4408
4408
 0
0
Revenge belongs to the class of Remote Access Trojans which means that it is usually used by the attackers to control infected PCs remotely or spy on the users by monitoring keystrokes and even computer surroundings through the remote webcam and microphone access.
Discovered for the first time in 2016, Revenge RAT continues to be a threat at the present day with a big spike in popularity monitored in 2019, when the malware was observed targeting corporations and government structures all around the world in a massive malicious campaign codenamed “Aggah”. Thanks to a large variety of distribution methods similar to ransomware, robust core feature-set, and solid persistence mechanisms, Revenge has become a popular choice for cybercriminals. The popularity of this RAT was further aided by its open-source nature – anybody can freely download Revenge on underground hacking forums and employ it in their own campaigns.
The Revenge RAT was first observed in the wild in June 2016, when it was released by a user with a nick Napoleon – an Arabic-speaking member of the underground hacking community.
The initial version of this malware was a simple malicious program that didn’t offer much, if any, code obfuscation and was mainly used by other Arabic-speaking cybercriminals. Despite the simplicity of the malware, at the time, only one out of 54 of VirusTotal scanners could pick up the malicious nature of the Revenge code, which confused the researchers bearing in mind the lack of anti-analysis techniques.
The creator used Visual Basic to develop this RAT and personally admitted that the malware was very bare-bones at the time of its initial release– providing only the most basic functions and definitely losing to competitors in terms of core feature-set. According to Napoleon, this explained why Revenge was available free of charge.
After two months since the initial release, a new version v0.2 was issued by the author, on a more popular hacking forum, this time with more features, but still offered completely free of charge. Since then Revenge has evolved even further and today, it offers cybercriminals a wide range of capabilities including remote files and registry alterations on an infected machine, access to memory, processes, and services as well as access to connected devices such as keyboards, webcams, and mice, allowing this malware to record the actions of its victims and collect information like banking credentials and social account data.
Core malicious feature-set was not the only thing that evolved over the course of the Revenge lifetime. Improvements in distribution and persistence made this threat truly a force to be reckoned with. In some campaigns, scripts were executed in the HTML of a custom Blogspot [com] page.
A video recorded in the ANY.RUN malware hunting service allows us to take a look at the execution of this malware as it unfolds and also other malicious programs like ransomware.
 Figure 1: Displays the lifecycle of Revenge in a visual form. A graph generated by ANY.RUN
Figure 1: Displays the lifecycle of Revenge in a visual form. A graph generated by ANY.RUN
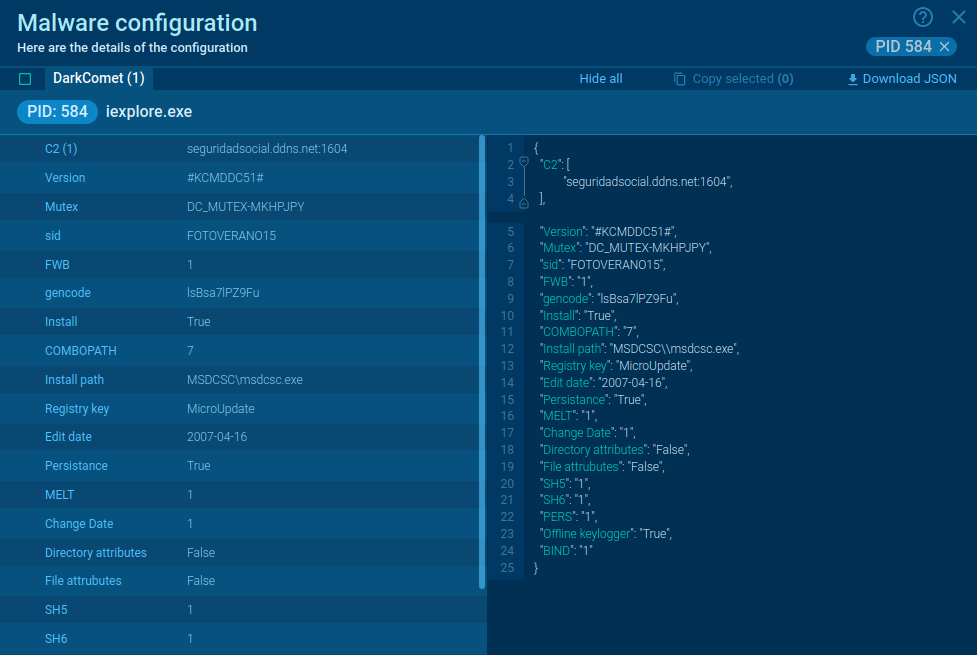
 Figure 2: Shows a customizable text report generated by the ANY.RUN malware analysis service which allows diving deeper into the details of the Revenge execution process.
Figure 2: Shows a customizable text report generated by the ANY.RUN malware analysis service which allows diving deeper into the details of the Revenge execution process.
Sometimes the first steps of Revenge trojan execution may vary depending on how it made its way into a victim's computer. The most common form of initial infiltration vector is by the use of Mshta.exe for downloading the payload or for direct execution from a URL. After the payload is delivered to the infected machine, Mshta.exe changes the autorun value in the registry and starts three processes - cmd.exe, powershell.exe and schtasks.exe. It starts cmd.exe to kill processes from a list, in the given example processes from the Microsoft Office packet were targeted. Powershell.exe is being launched to download the main payload. In turn, schtasks.exe is launched in a way to generate a scheduled task that provides Revenge persistence in the infected system. After all these steps, the malware is ready to complete commands from C2 servers.
The best line of defense against threats like Revenge RAT is to keep a security product installed and updated with the latest firmware. One should not disable native Windows security features, regularly update the OS and adhere to the best security practices of staying safe online.
As such, it is advised to stay clear of downloading email attachments from unknown senders and never enabling macros in Microsoft Office if prompted to do so by a file downloaded from a suspicious email. The same advice comes for other threats like Glupteba and Smoke Loader.
Revenge has been seen being distributed in a variety of ways the same as ransomware, some of which are potentially more effective than others. For example, Revenge is known to infect PCs from malicious email attachments and corrupted ads on compromised websites.
Most commonly, once delivered in the Microsoft Office file that was downloaded and launched by the potential victim, Revenge will use macros to connect to an outside domain, sometimes hidden on a web page, from which additional scripts and content are downloaded until the actual malware is installed on the PC.
Analysts can get information about which MITRE ATT&CK™ MATRIX techniques were applied by malware. Just click on the "ATT&CK™ MATRIX " button.
 Figure 3: Revenge MITRE ATT&CK MATRIX techniques
Figure 3: Revenge MITRE ATT&CK MATRIX techniques
Revenge is no slouch when it comes to Remote Banking Trojans. It has begun its lifespan as a simplistic malware such as ransomware and without anti-analysis features but has evolved to become a capable and persistent trojan used in massive attacks in Europe, North America, Asia, and the Middle East.
The popularity of this malware is not only due to its robust feature-set, but also ready availability since Revenge can be downloaded for free from a number of underground communities.
Professionals can establish a secure cyber defense against Revenge and similar RATs and secure their corporate or government networks by reverse engineering and studying a threat using malware hunting services like to ANY.RUN.